
CALGreen Services for City of Sonoma
The City of Sonoma has also adopted the CALGreen green building code to promote sustainable construction practices and reduce the environmental impact of new developments.

The City of Sonoma has also adopted the CALGreen green building code to promote sustainable construction practices and reduce the environmental impact of new developments.

City of Santa Rosa has implemented stringent green building codes in line with the statewide CALGreen program. Santa Rosa is committed to reducing the environmental impact of new developments and promoting sustainable construction practices.

This article will discuss the CALGreen Services for San Rafael

The City of Napa has also adopted a stringent form of CALGreen green building code to reduce the environmental impact of new construction and promote

The Dual Fuel Heat Pump is a combination of both heating and cooling systems which consists of electric heat pump and a gas furnace. The major heating load is addressed by the heat pump as it is more efficient than the gas furnace.
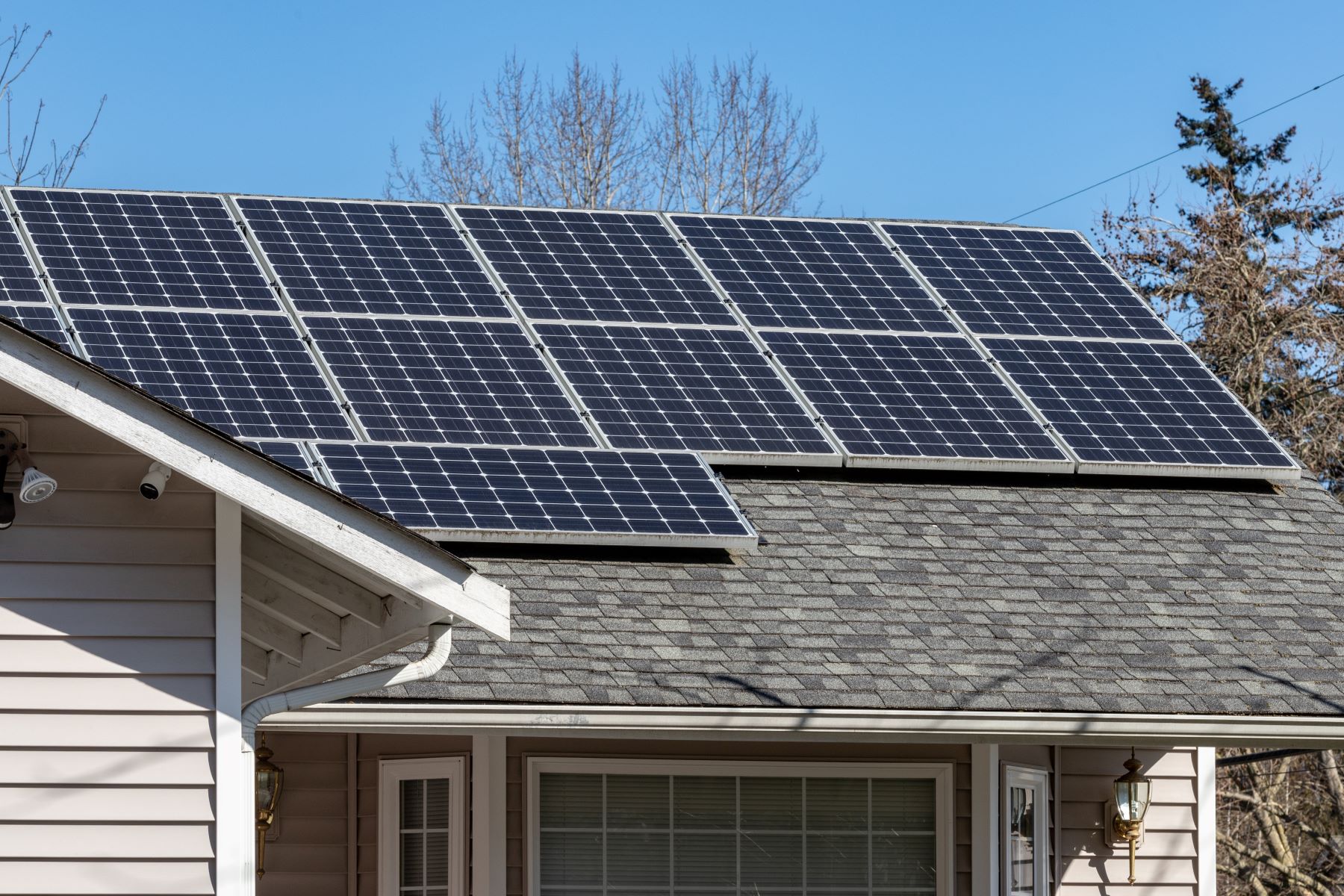

CALGreen – City of Palo Alto has implemented one of the most aggressive green building codes in the state of California. Due to very high value of real estate and heightened awareness for sustainable construction practices among the residents, city has succeeded in justifying the enforcement of green building code that few other cities in the state of California have enforced.

California, a renowned leader in environmental protection, has implemented CALGreen, a comprehensive green building code that sets mandatory standards for sustainable construction.
California is a state known for its commitment to sustainability and environmental protection. One of the ways it achieves this is through the implementation of Title 24, a set of building energy efficiency standards.

California has long been a leader in environmental protection, and its commitment to sustainability is evident through its progressive building code: Title 24.
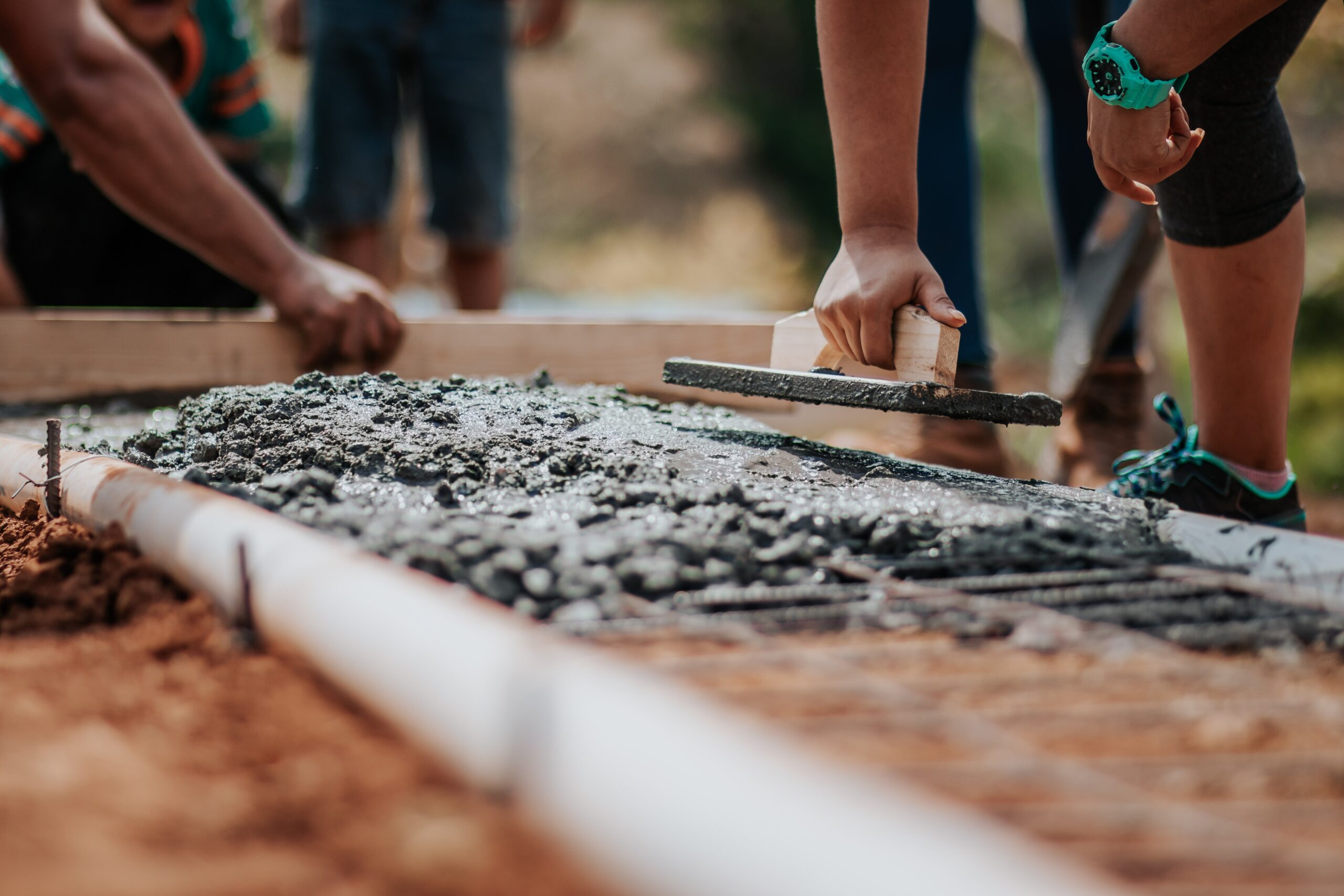

CALGreen Code Section A5.405.5: Cement and concrete.
Use cement and concrete made with recycled products and complying with the following sections:
CALGreen Code Section A5.405.5.1: Cement.
The City of Sonoma has also adopted the CALGreen green building code to promote sustainable construction practices and reduce the environmental impact of new developments.
City of Santa Rosa has implemented stringent green building codes in line with the statewide CALGreen program. Santa Rosa is committed to reducing the environmental impact of new developments and promoting sustainable construction practices.
This article will discuss the CALGreen Services for San Rafael
The City of Napa has also adopted a stringent form of CALGreen green building code to reduce the environmental impact of new construction and promote
The Dual Fuel Heat Pump is a combination of both heating and cooling systems which consists of electric heat pump and a gas furnace. The major heating load is addressed by the heat pump as it is more efficient than the gas furnace.
CALGreen – City of Palo Alto has implemented one of the most aggressive green building codes in the state of California. Due to very high value of real estate and heightened awareness for sustainable construction practices among the residents, city has succeeded in justifying the enforcement of green building code that few other cities in the state of California have enforced.
California, a renowned leader in environmental protection, has implemented CALGreen, a comprehensive green building code that sets mandatory standards for sustainable construction.
California is a state known for its commitment to sustainability and environmental protection. One of the ways it achieves this is through the implementation of Title 24, a set of building energy efficiency standards.
California has long been a leader in environmental protection, and its commitment to sustainability is evident through its progressive building code: Title 24.
CALGreen Code Section A5.405.5: Cement and concrete.
Use cement and concrete made with recycled products and complying with the following sections:
CALGreen Code Section A5.405.5.1: Cement.
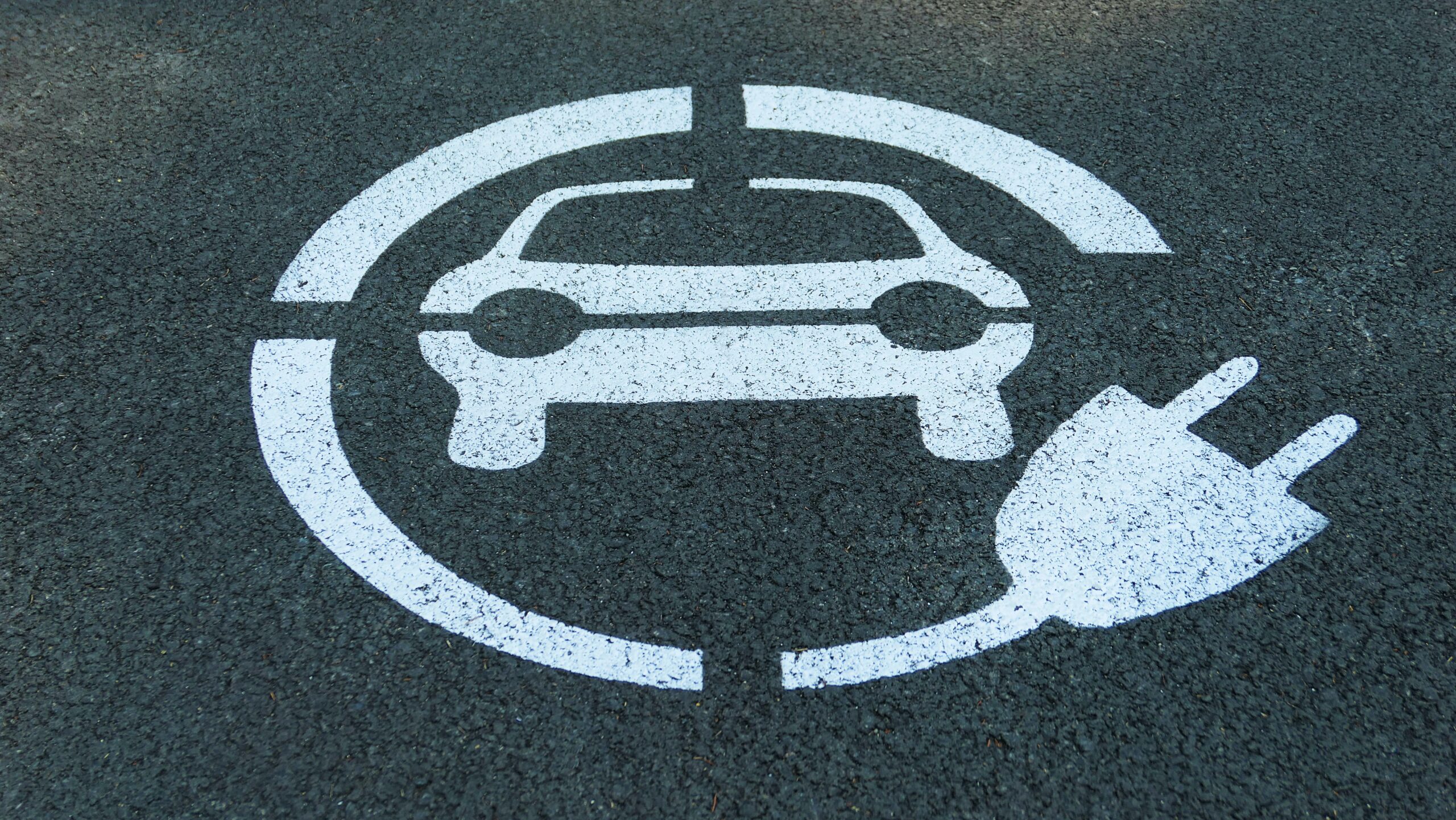

Several measures have been included in the CALGreen code to encourage the use of Clean Air Vehicles. Allocation of parking spaces reserved for such vehicles is one of them. This is a mandatory measure for all new construction and addition/alteration projects that are adding parking spaces.
Energy efficiency has never been more critical, and California is leading the way in the United States with its innovative energy standards and regulations. Title
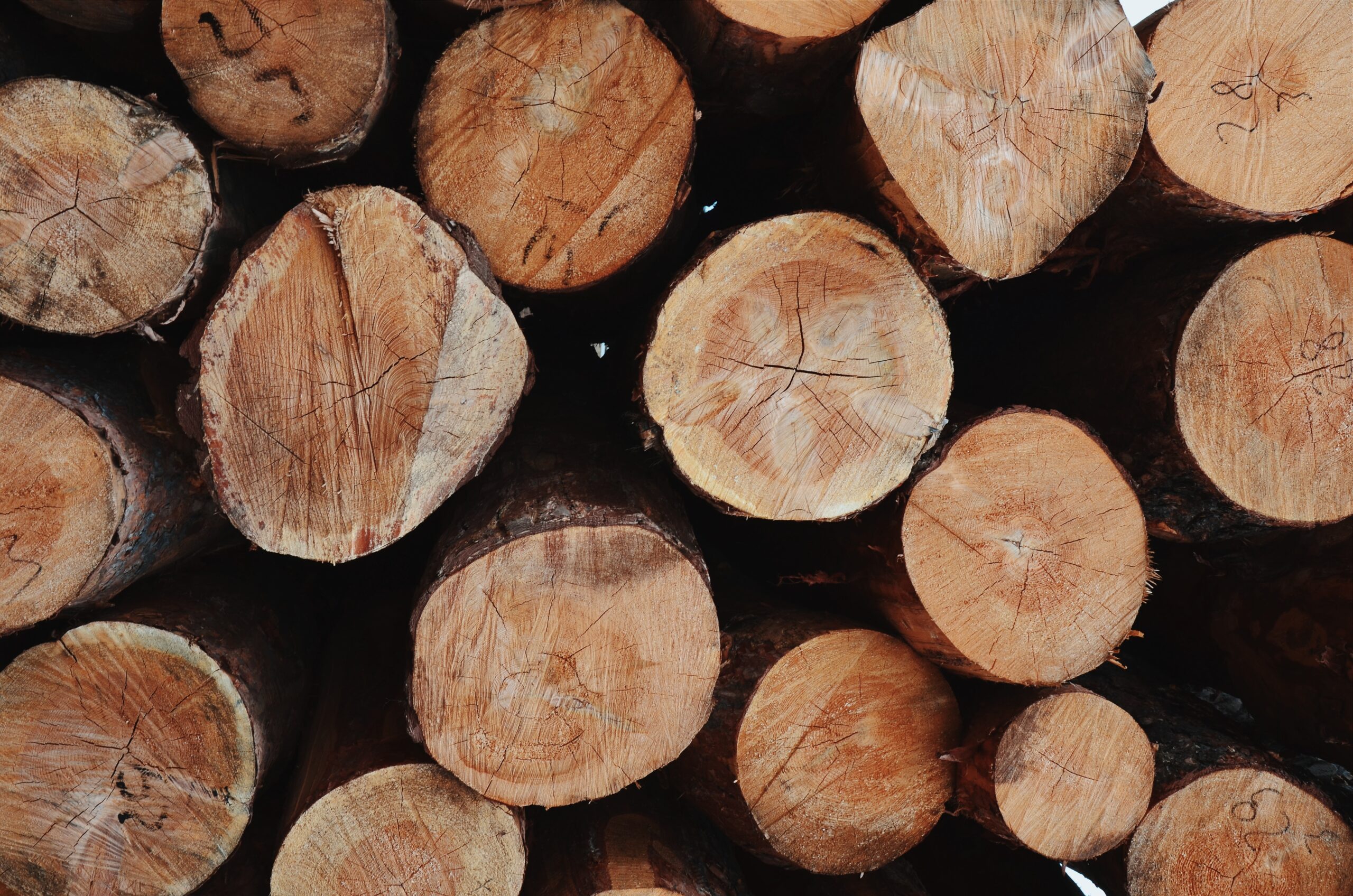

The purpose of the measure is to save energy in relation to the transportation of construction materials over long distances to the construction site.

A Title 24 report typically refers to the energy efficiency standards in California, also known as the California Energy Code. The Title 24 report is required for new construction and major renovations of residential and non-residential buildings in California to ensure they meet specific energy efficiency standards.

Title 24 refers to a set of building energy efficiency standards in the state of California, United States. The title is part of the California Code of Regulations and is officially known as the California Building Standards Code, Title 24. The standards were established to promote energy efficiency and environmental sustainability in new construction and major renovations of residential and non-residential buildings.

A JADU (Junior Accessory Dwelling Unit) is a specific type of accessory dwelling unit (ADU) in California. It is a small, self-contained living unit that is created within an existing single-family home. The main distinction between a JADU and other types of ADUs is that a JADU is created within the existing space of the primary residence, typically by converting a part of the house, such as a bedroom or a portion of the living area.

Title 24 refers to a set of building energy efficiency standards in the state of California, United States. These standards are established by the California Energy Commission (CEC) and are part of the California Code of Regulations.

CALGreen – In an effort to preserve water quality, these techniques aim to reduce storm water runoff volume and rate. The discharge of surface water contaminants from the project site into receiving waterways can be avoided by making sure that there is no detectable increase.

CALGreen – To limit thermal bridging between materials that come into contact with steel framing and to reduce the quantity of steel that must be utilized in a steel framing system.

CALGreen – To maximize open space inside a development and to promote the use of plants whenever it is possible. The inclusion of these clauses can enhance groundwater recharge, preserve open space and wildlife habitats, and increase the carbon sink effect, which lowers greenhouse gas emissions.
The City of Sonoma has also adopted the CALGreen green building code to promote sustainable construction practices and reduce the environmental impact of new developments.
City of Santa Rosa has implemented stringent green building codes in line with the statewide CALGreen program. Santa Rosa is committed to reducing the environmental impact of new developments and promoting sustainable construction practices.
This article will discuss the CALGreen Services for San Rafael
The City of Napa has also adopted a stringent form of CALGreen green building code to reduce the environmental impact of new construction and promote
The Dual Fuel Heat Pump is a combination of both heating and cooling systems which consists of electric heat pump and a gas furnace. The major heating load is addressed by the heat pump as it is more efficient than the gas furnace.
CALGreen – City of Palo Alto has implemented one of the most aggressive green building codes in the state of California. Due to very high value of real estate and heightened awareness for sustainable construction practices among the residents, city has succeeded in justifying the enforcement of green building code that few other cities in the state of California have enforced.
California, a renowned leader in environmental protection, has implemented CALGreen, a comprehensive green building code that sets mandatory standards for sustainable construction.
California is a state known for its commitment to sustainability and environmental protection. One of the ways it achieves this is through the implementation of Title 24, a set of building energy efficiency standards.
California has long been a leader in environmental protection, and its commitment to sustainability is evident through its progressive building code: Title 24.
CALGreen Code Section A5.405.5: Cement and concrete.
Use cement and concrete made with recycled products and complying with the following sections:
CALGreen Code Section A5.405.5.1: Cement.